

The infobar text, slider and 1px coloured image border all indicate which channel is selected. IMPORTANT! The nav bar still selects the active channel, and that is where measurements / maniplulations are applied! Draw a ROI on a bright area and Measure ('m').Use the check boxes (channels tool) to turn channels off.In this image, each channel already has an associated Look Up Table (LUT) Navigate through the channels then run Channels Tool and change to Greyscale.You will very rarely have to deal with Interleaved stacks because of Hyperstacks which give you independent control of dimensions with additional control bars.Ĭonvert between stack types with the menu When more than one dimension (time, z, channel) is included, the images are still stored in a linear stack so it's critical to know the dimension order (eg, XYCZT, XYZTC etc) so you can navigate the stack correctly. TIF) can store multiple images in one file which are called stacks Stacks Understanding how Fiji deals with multidimensional images TL DR: pixels can have non-integer values which can be useful in applications like ratiometric imaging. For another way to approach this, see Overlaysģ2 bit is a special data type called floating point. Pick a non-white colour for the scale bar.Check the image is calibrated (infobar or ).Values falling beyond the new White point are dumped into the top bin of the histogram (IE 256 in an 8-bit image) and information from the image is lost If we repeat the same manipulation, the maximum intensity value in the image is now outside the bounds of the display scale! The histogram is now stretched and the intensity value of every pixel is effectively doubled which increases the contrast in the image Contrast: distance between the black and white point.Brightness: horizontal position of the display window.The Black and White points of the histogram dictate the bounds of the display (changing these values alters the brightness and contrast of the image) Photos typically have a broad range of intensity values and so the distribution of intensities varies greatlyįluorescent micrographs will typically have a much more predicatble distribution: The intensity histogram shows the number (on the y-axis) of each intensity value (on the x-axis) and thus the distribution of intensities The spatial calibration can be in any unit you like but (almost) all subsequent measurements will use that unit!īasic Manipulations Intensity and Geometric adjustments.Running also allows you to view and set calibration.The Infobar is a great way to tell if your image is calibrated.statusbar (right bottom): gives current cursor coordinates and intensity readout.infobar (right top): gives info on the image.command is very useful when opening multiple images.Hit 'Enter' to bring the Fiji window to the front.When zoomed in, pan by holding space and click-dragging with mouse.Open 01-Photo.tif and 02-Biological_Image.tif.Hands on With Fiji Getting to know the interface, info & status bars, calibrated vs non-calibrated images ImageJ is a java program for image processing and analysis. Unless you have good reason not to, always collect data at the highest possible bit depth Introduction to ImageJ & Fiji A cross platform, open source, Java-based image processing program The A/D converter determines the dynamic range of the data
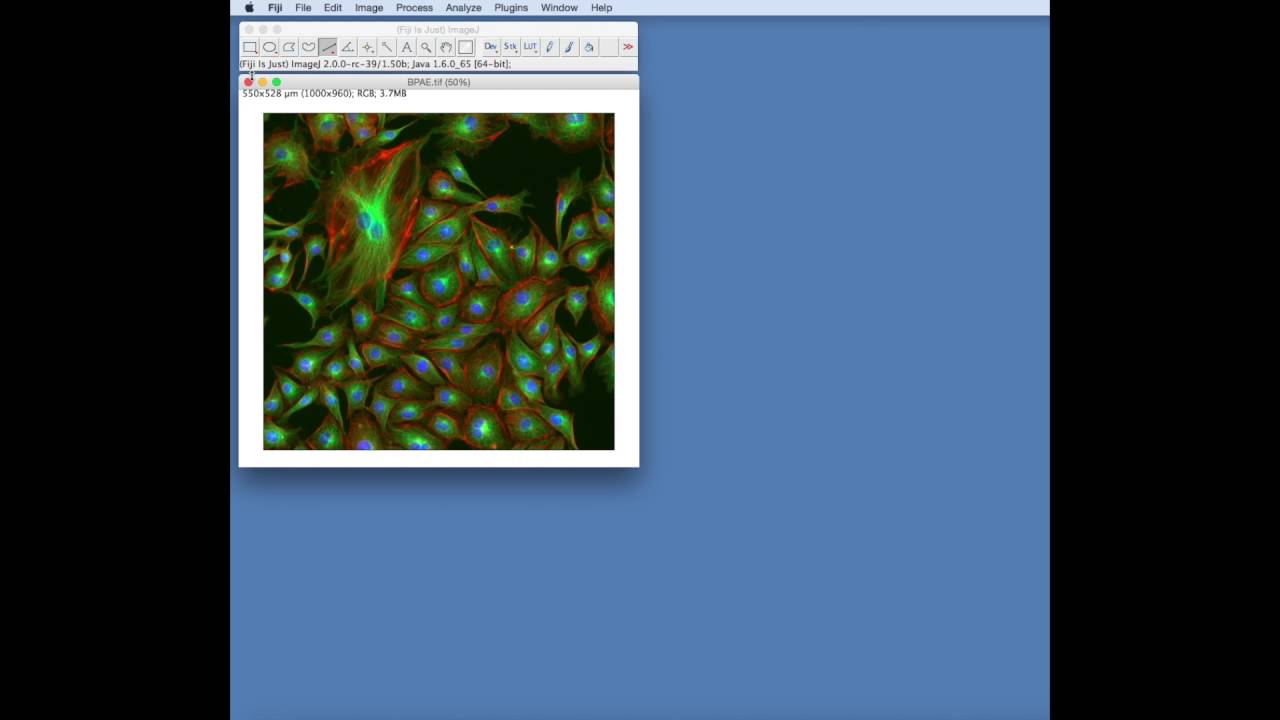
Widefield and laser-scanning microscopes acquire images in different ways.ĭetectors collect photons and convert them to a voltage


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
